ARTICLE AD BOX
A University of Pittsburgh study indicates that readers can't tell the difference between poems written by AI and those written by humans. The research shows that people actually rate computer-generated verses higher than works by famous poets like Shakespeare, but only if they don't know who wrote them.
In a large-scale test with 16,340 participants, people correctly identified AI versus human-written poems only 46.6 percent of the time—worse than chance. Even more striking, participants mistook AI-generated poems for human work more often than they mistook actual human-written verses.
The research team used ChatGPT 3.5 to create five poems that mimicked the style of ten famous English-language poets, including William Shakespeare, Walt Whitman, and Emily Dickinson, and then asked participants to rate these AI creations as well as authentic poems by these authors.
"We found that AI-generated poems were rated more favorably in qualities such as rhythm and beauty, and that this contributed to their mistaken identification as human-authored," write study authors Brian Porter and Edouard Machery.
Ad
THE DECODER Newsletter
The most important AI news straight to your inbox.
✓ Weekly
✓ Free
✓ Cancel at any time
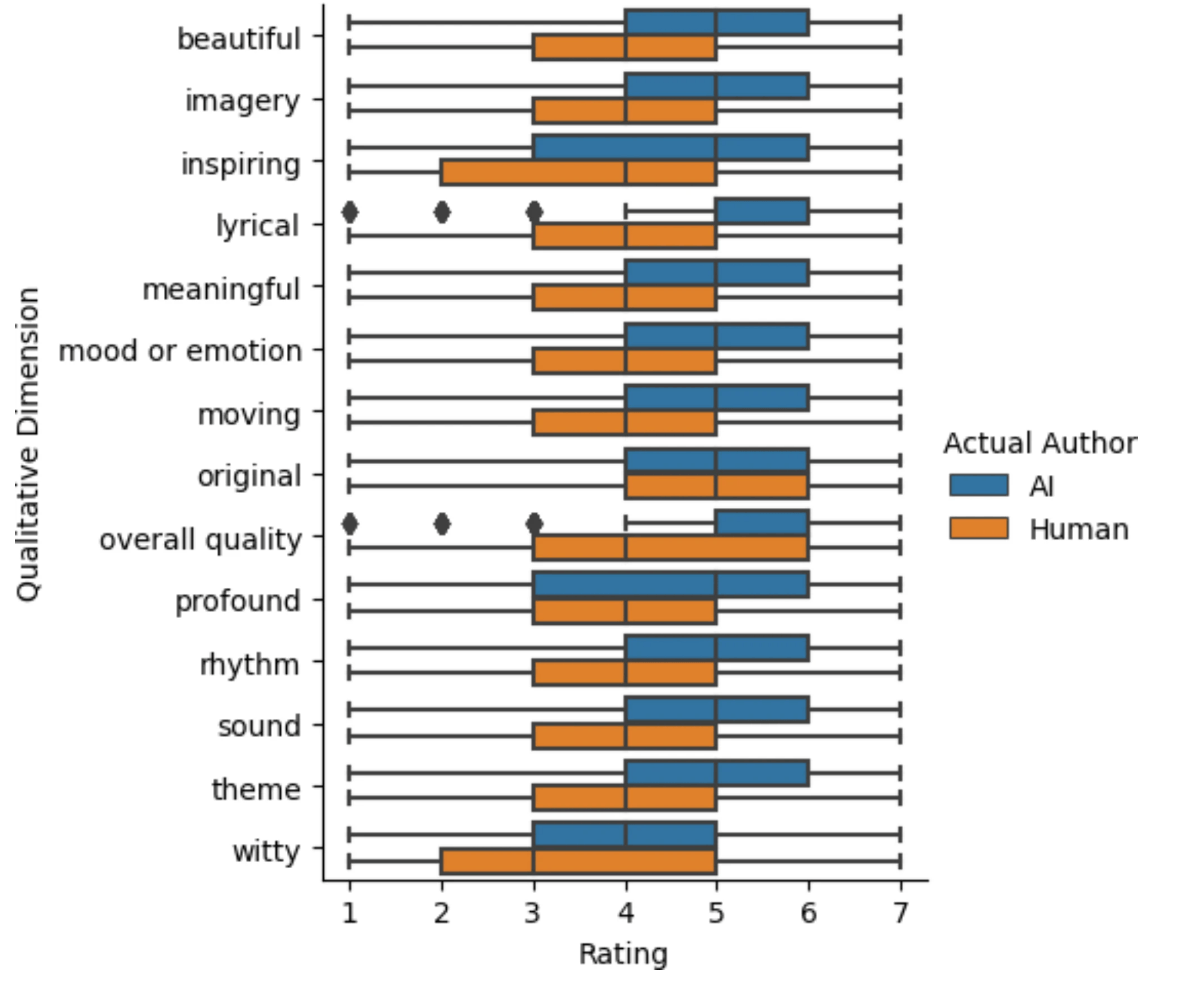 Across 13 different quality metrics, from beauty to wit, the AI poems matched or exceeded human works. The computer-generated verses stood out particularly in technical aspects like rhythm and sound. | Graphic: Porter, Machery
Across 13 different quality metrics, from beauty to wit, the AI poems matched or exceeded human works. The computer-generated verses stood out particularly in technical aspects like rhythm and sound. | Graphic: Porter, MacherySimpler language gives AI an edge
The researchers point to one possible explanation: AI poems use more direct, accessible language that non-experts find easier to understand. Participants in the study "mistakenly interpret their own preference for a poem as evidence that it is human-written," the researchers note.
In a follow-up experiment with 696 participants, poems labeled as AI-generated received lower ratings—a pattern seen in other creative fields. When analyzing four key factors—creativity, mood, structure, and emotional quality—ratings stayed surprisingly balanced between AI and human authors when the source wasn't revealed.
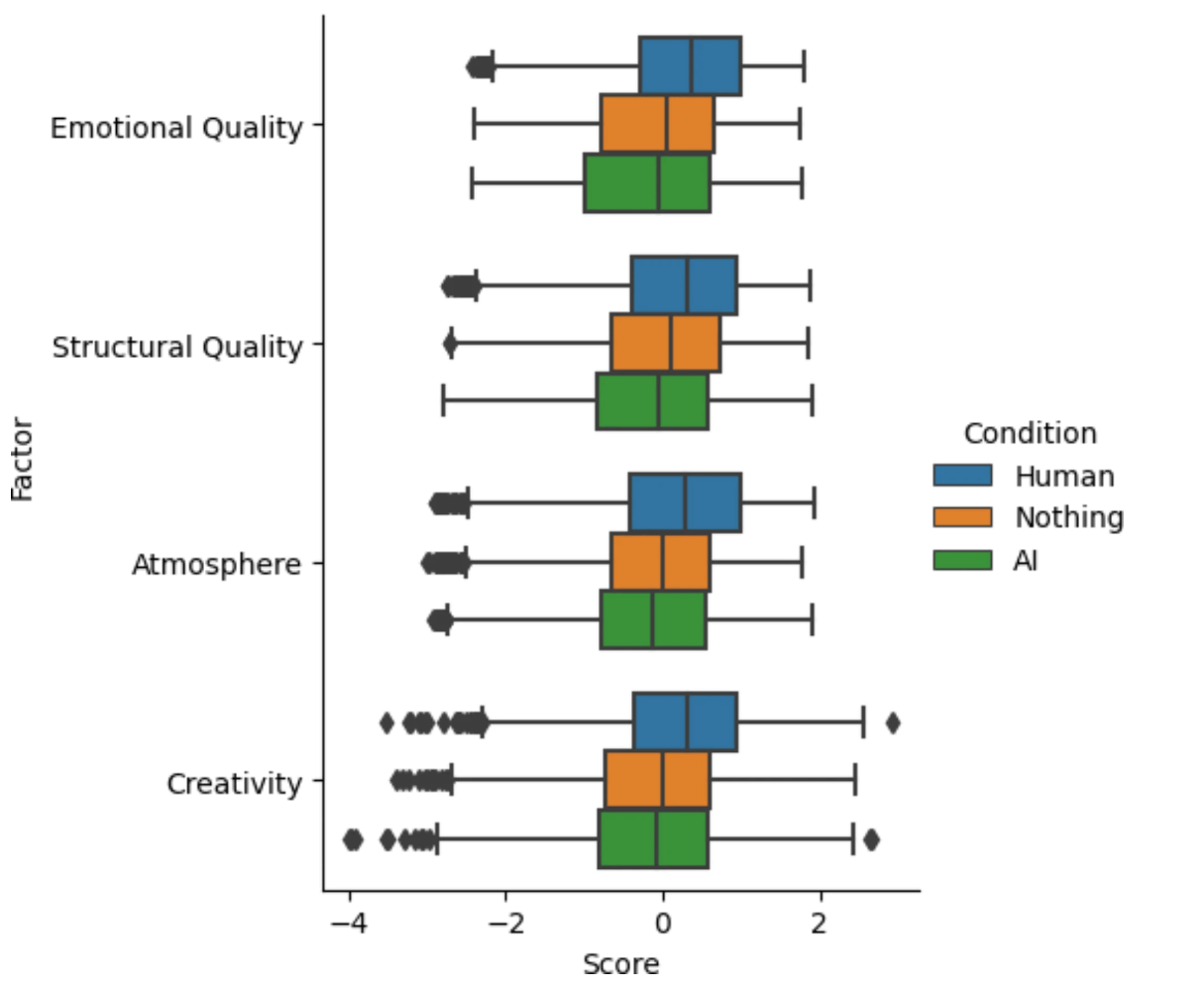 When source attribution is hidden (orange), readers rate AI and human-written poems nearly identically across emotional, structural, atmospheric, and creative dimensions. This suggests our biases about AI creativity may be more influential than actual quality differences. | Graphic: Porter, Machery
When source attribution is hidden (orange), readers rate AI and human-written poems nearly identically across emotional, structural, atmospheric, and creative dimensions. This suggests our biases about AI creativity may be more influential than actual quality differences. | Graphic: Porter, MacheryTwo key points frame these findings: First, the study used ChatGPT 3.5, now an older version of the AI model. Newer versions might produce even more convincing poems.
Second, the AI poems specifically imitated existing poets' styles rather than creating entirely original work. Without these human templates, the AI-generated poems might look very different.
The researchers also note their study focused on "non-experts," who likely responded well to AI's simpler language. Poetry experts would likely spot differences more easily, given their deeper knowledge of poetic structure, rhyme, and meter.
Recommendation

 11 months ago
21
11 months ago
21